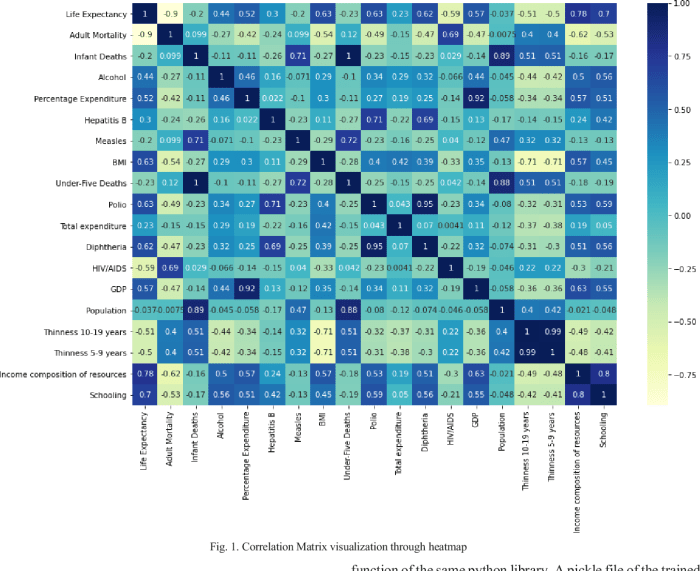
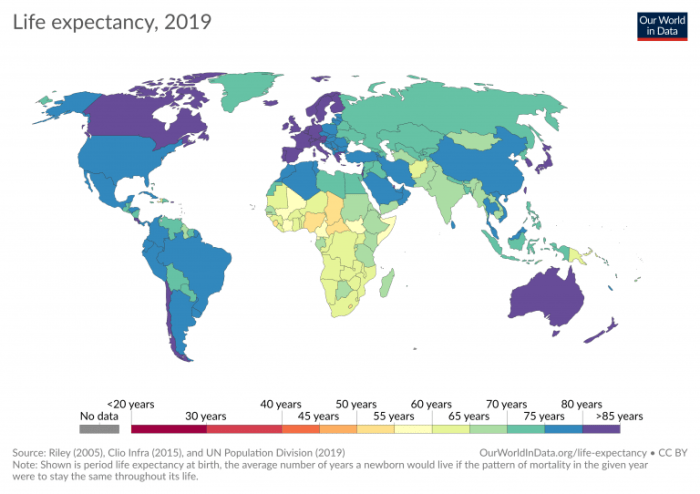
Life expectancy ap human geography example – Life expectancy, a crucial indicator of human development, takes center stage in human geography. This article delves into the intricate patterns and variations of life expectancy globally, regionally, and temporally, exploring its profound implications for understanding human well-being and socioeconomic conditions.
From examining the factors shaping life expectancy disparities to analyzing its applications in healthcare planning and social welfare programs, this comprehensive analysis sheds light on the multifaceted nature of life expectancy and its significance in human geography.
Global Patterns of Life Expectancy: Life Expectancy Ap Human Geography Example
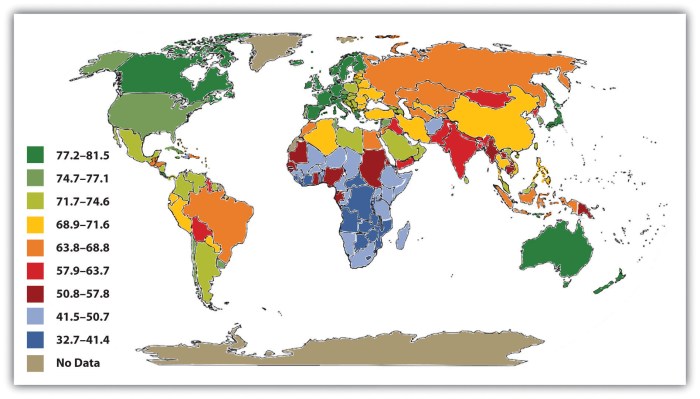
Life expectancy, a measure of the average number of years a person is expected to live, varies significantly across the globe. Factors such as socioeconomic conditions, healthcare access, and environmental factors influence these patterns. Higher life expectancies are generally observed in developed countries with strong economies, advanced healthcare systems, and stable political environments.
In contrast, lower life expectancies are found in developing countries, often due to limited access to healthcare, poor nutrition, and environmental hazards. Geographic factors, such as altitude and climate, can also impact life expectancy.
Regional Variations in Life Expectancy
Regions with high life expectancies include Europe, North America, and East Asia. Countries in these regions have made significant progress in healthcare, education, and economic development. In contrast, regions with low life expectancies include sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and parts of Southeast Asia.
These regions face challenges such as poverty, political instability, and limited access to healthcare.
Temporal Trends in Life Expectancy
Life expectancy has increased globally over time, particularly in the last century. Medical advancements, public health measures, and improved living conditions have contributed to this increase. However, the rate of improvement has varied across regions, with some countries experiencing faster gains than others.
Life Expectancy and Human Geography
Life expectancy is an important indicator of human development. It reflects the overall well-being of a population and is influenced by factors such as education, income, and access to healthcare. Higher life expectancies are generally associated with higher levels of human development.
Examples of Life Expectancy Data Analysis, Life expectancy ap human geography example
Life expectancy data has been used in various human geography research studies. For example, researchers have analyzed life expectancy trends to identify areas with health disparities and to evaluate the effectiveness of public health interventions. Life expectancy data has also been used to project future population growth and to plan for healthcare services.
Applications of Life Expectancy Analysis
Life expectancy analysis has practical applications in healthcare planning, policymaking, and social welfare programs. For example, life expectancy data can be used to estimate future healthcare needs and to allocate resources accordingly. It can also be used to identify populations at risk of premature death and to develop targeted interventions to improve their health outcomes.
Quick FAQs
What are the key factors influencing global patterns of life expectancy?
Socioeconomic conditions, healthcare access, environmental factors, political stability, and cultural practices.
How has life expectancy changed over time?
Life expectancy has generally increased over time due to medical advancements, public health measures, and lifestyle changes.
What are the applications of life expectancy analysis in human geography?
Healthcare planning, policymaking, social welfare programs, and understanding human development.