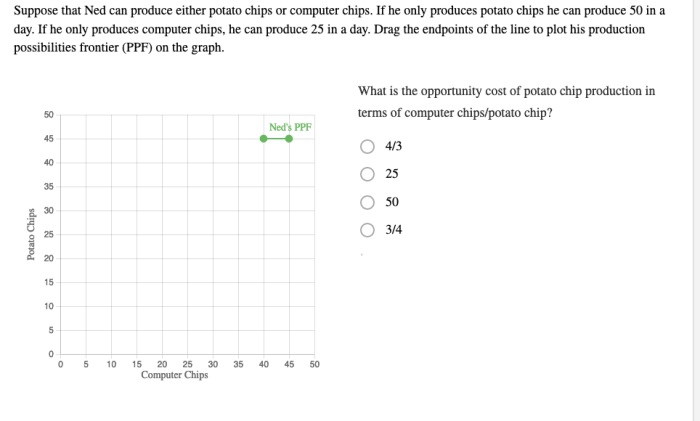
Suppose that Ned can produce either apples or oranges. This simple scenario provides a valuable framework for understanding fundamental economic concepts such as production possibilities, factors of production, comparative advantage, and economic efficiency. By examining Ned’s choices, we gain insights into the complexities of production and the allocation of resources.
Ned’s production possibilities frontier illustrates the various combinations of apples and oranges he can produce with his given resources. The opportunity cost of producing one good is the amount of the other good that must be sacrificed. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for making optimal production decisions.
Production Possibilities: Suppose That Ned Can Produce Either
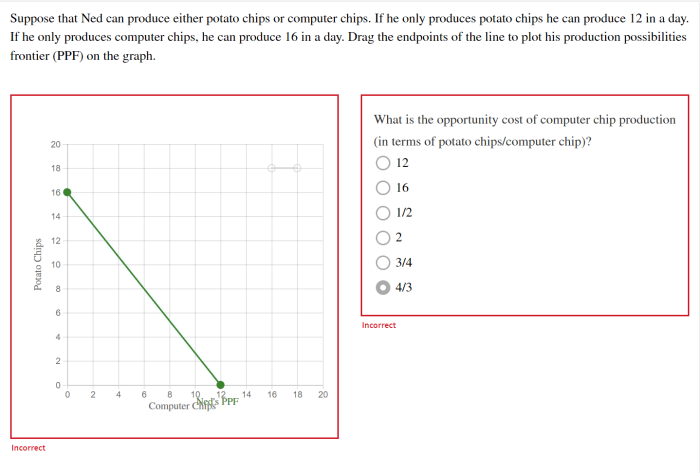
The production possibilities frontier (PPF) is a graphical representation of the maximum combinations of two goods that an economy can produce with its given resources and technology. In Ned’s case, his PPF shows the maximum combinations of apples and oranges he can produce.
The PPF is downward sloping, which means that Ned cannot produce more of one good without sacrificing some of the other. The opportunity cost of producing one more apple is the number of oranges that Ned must give up.
Factors of Production
The factors of production are the resources that Ned uses to produce goods. These include land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship.
- Landis the natural resources that Ned uses to produce goods, such as his orchard.
- Laboris the human effort that Ned uses to produce goods, such as his own labor and the labor of any hired workers.
- Capitalis the physical assets that Ned uses to produce goods, such as his tools, equipment, and buildings.
- Entrepreneurshipis the ability to combine the other factors of production to produce goods.
The availability of these factors of production affects Ned’s production possibilities. For example, if Ned has more land, he can produce more apples and oranges. If Ned has more labor, he can produce more of both goods. If Ned has more capital, he can produce more of both goods more efficiently.
Comparative Advantage
Comparative advantage is the ability of a country or individual to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than another country or individual. In Ned’s case, he has a comparative advantage in producing apples if he can produce apples at a lower opportunity cost than oranges.
Ned can specialize in producing apples and trade with others who have a comparative advantage in producing oranges. This will allow Ned to produce more goods overall than if he tried to produce both goods himself.
Economic Efficiency, Suppose that ned can produce either
Economic efficiency is the ability of an economy to produce the maximum amount of goods and services with the resources it has. Ned can achieve economic efficiency by producing on his PPF and by using his resources efficiently.
Ned can improve his economic efficiency by:
- Using his resources more efficiently.For example, Ned could use better farming techniques to increase his crop yield.
- Specializing in producing goods that he has a comparative advantage in.As discussed above, this will allow Ned to produce more goods overall.
- Trading with others.This will allow Ned to get goods that he cannot produce himself at a lower cost.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the factors of production that Ned uses?
Ned uses land, labor, and capital to produce apples and oranges.
How does comparative advantage affect Ned’s production?
Comparative advantage suggests that Ned should specialize in producing the good for which he has a lower opportunity cost. This allows him to maximize his total output.
What is economic efficiency, and how does it relate to Ned’s production?
Economic efficiency occurs when Ned produces the optimal combination of goods, given his resources. To achieve efficiency, he must operate on his production possibilities frontier.