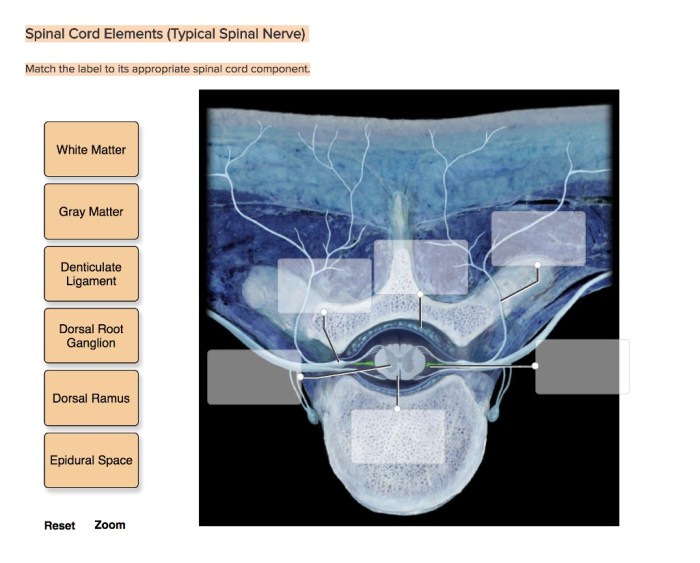
Match the label to its appropriate spinal cord component. The spinal cord is a long, thin, cylindrical structure that extends from the brainstem to the lower back. It is responsible for transmitting sensory and motor signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
The spinal cord is also involved in a number of reflex actions, which are automatic responses to stimuli that do not require conscious thought.
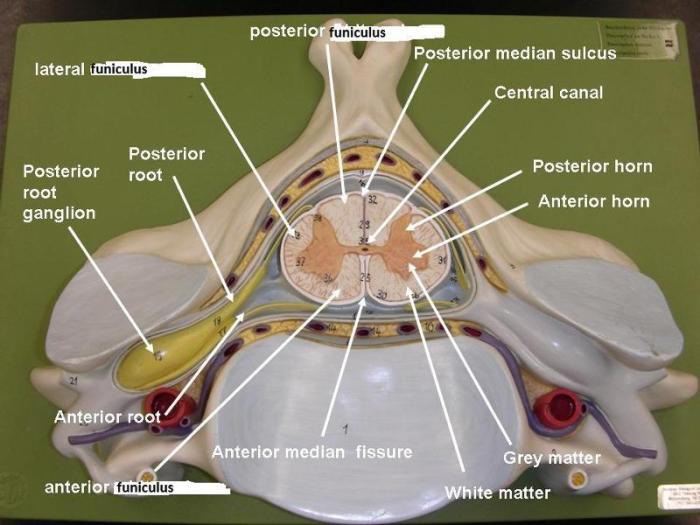
The spinal cord is divided into two main regions: the gray matter and the white matter. The gray matter is located in the center of the spinal cord and contains the cell bodies of neurons. The white matter is located on the outside of the spinal cord and contains the axons of neurons.
The axons are long, thin fibers that transmit electrical signals between neurons.
Sensory Pathways
The spinal cord contains several sensory pathways that transmit information from the body to the brain. These pathways can be classified into three main groups: ascending tracts, descending tracts, and local circuits.
Ascending Tracts, Match the label to its appropriate spinal cord component.
- Posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway:Transmits fine touch, proprioception, and vibration sense from the body to the brain.
- Spinothalamic pathway:Transmits pain, temperature, and crude touch from the body to the brain.
- Dorsal column pathway:Transmits fine touch and proprioception from the body to the brain.
Descending Tracts
- Corticospinal tract:Transmits voluntary motor commands from the brain to the spinal cord.
- Vestibulospinal tract:Transmits information from the vestibular system to the spinal cord, helping to maintain balance.
- Reticulospinal tract:Transmits information from the reticular formation to the spinal cord, helping to control muscle tone and posture.
Local Circuits
Local circuits are short, interneuronal pathways that connect sensory neurons to motor neurons within the spinal cord. These circuits are responsible for reflex actions, which are automatic responses to stimuli that do not require conscious thought.
Motor Pathways
The spinal cord contains several motor pathways that transmit information from the brain to the muscles. These pathways can be classified into two main groups: upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons.
Upper Motor Neurons
Upper motor neurons are long, myelinated neurons that originate in the brain and terminate in the spinal cord. They transmit voluntary motor commands from the brain to the lower motor neurons.
Lower Motor Neurons
Lower motor neurons are short, unmyelinated neurons that originate in the spinal cord and terminate in the muscles. They transmit motor commands from the upper motor neurons to the muscles, causing them to contract.
Reflex Arcs: Match The Label To Its Appropriate Spinal Cord Component.
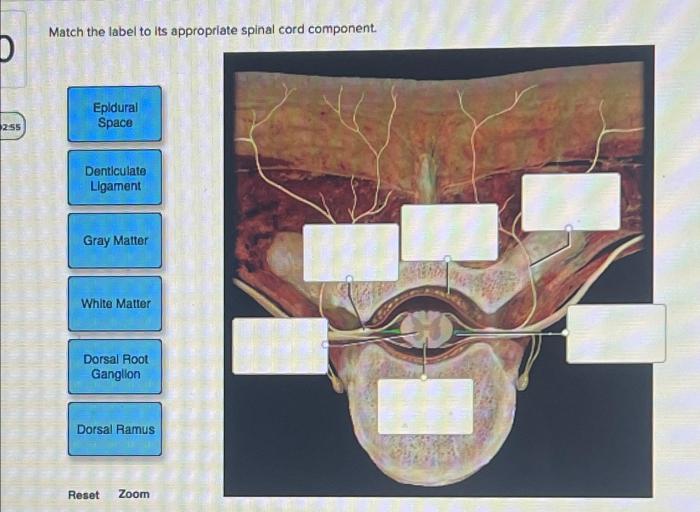
Reflex arcs are neural pathways that mediate reflex actions. A reflex arc consists of a sensory neuron, an interneuron, and a motor neuron.
When a stimulus is applied to the body, the sensory neuron detects the stimulus and sends a signal to the spinal cord. The interneuron then processes the signal and sends a signal to the motor neuron. The motor neuron then sends a signal to the muscle, causing it to contract.
Reflex arcs are important for protecting the body from harm. For example, the knee-jerk reflex helps to protect the knee from injury by causing the leg to extend when the patellar tendon is tapped.
FAQ Explained
What is the function of the spinal cord?
The spinal cord is responsible for transmitting sensory and motor signals between the brain and the rest of the body. It is also involved in a number of reflex actions, which are automatic responses to stimuli that do not require conscious thought.
What are the two main regions of the spinal cord?
The two main regions of the spinal cord are the gray matter and the white matter. The gray matter is located in the center of the spinal cord and contains the cell bodies of neurons. The white matter is located on the outside of the spinal cord and contains the axons of neurons.
What is the difference between gray matter and white matter?
The gray matter contains the cell bodies of neurons, while the white matter contains the axons of neurons. The axons are long, thin fibers that transmit electrical signals between neurons.