In a competitive market when there is no deadweight loss – In the realm of economics, competitive markets are often lauded for their efficiency. However, the presence of deadweight loss can undermine this efficiency, leading to suboptimal outcomes for consumers and producers. This article delves into the concept of deadweight loss in competitive markets, exploring its causes, consequences, and the conditions necessary for its absence.
By understanding these dynamics, we can gain valuable insights into the functioning of competitive markets and the role of government policies in promoting market efficiency.
Market Dynamics in Competitive Environments
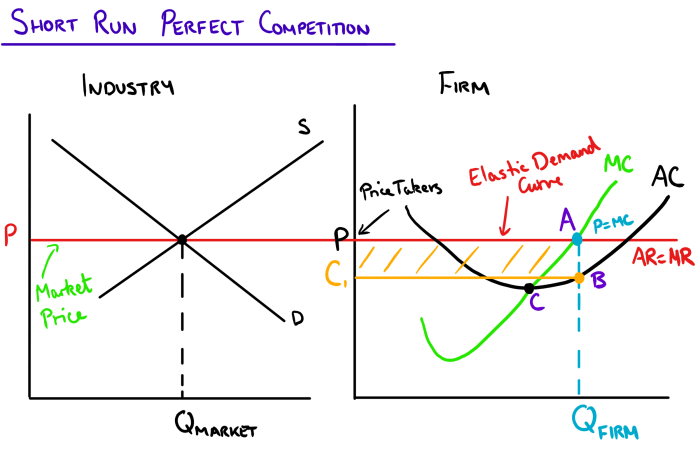
In competitive markets, numerous buyers and sellers interact, leading to a market equilibrium where the forces of supply and demand determine prices and quantities.
Industries that exhibit competitive market structures include agriculture, commodities trading, and financial markets.
Supply and demand play a crucial role in shaping market outcomes. When supply exceeds demand, prices fall, incentivizing producers to reduce supply. Conversely, when demand exceeds supply, prices rise, encouraging producers to increase supply.
Deadweight Loss: Definition and Causes, In a competitive market when there is no deadweight loss
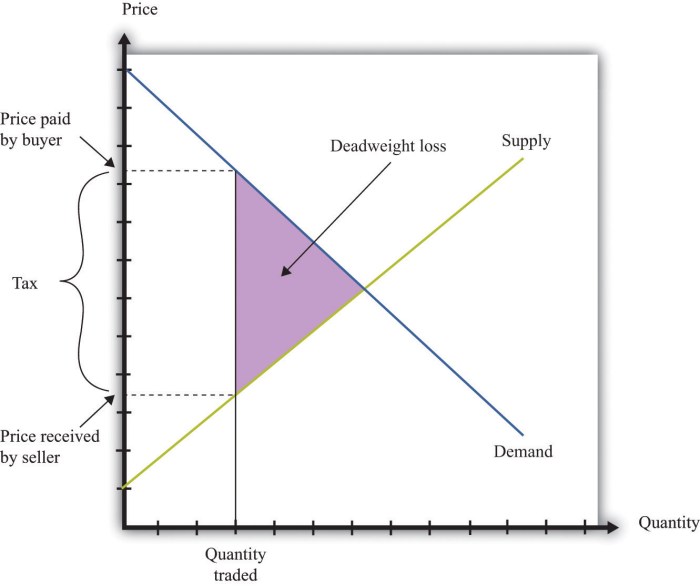
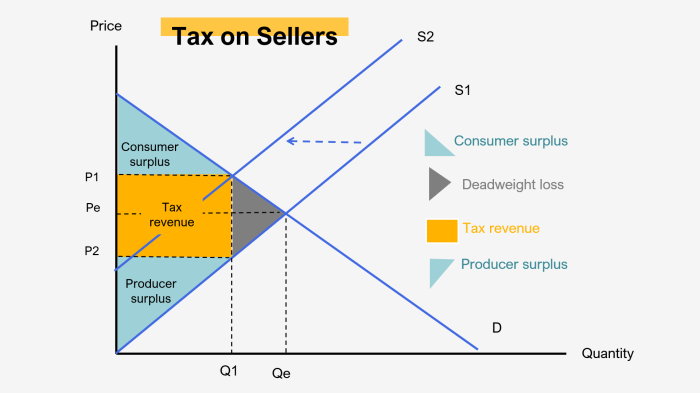
Deadweight loss refers to the reduction in economic efficiency that occurs when market outcomes deviate from the socially optimal level.
Factors that contribute to deadweight loss include:
- Government interventions, such as price ceilings or subsidies
- Market imperfections, such as monopolies or externalities
Deadweight loss affects consumer and producer surplus by reducing the overall value created in the market.
Absence of Deadweight Loss: Conditions and Implications
For a competitive market to operate without deadweight loss, the following conditions must be met:
- Perfect competition: Many buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, and perfect information
- No externalities: Production or consumption does not affect third parties
The absence of deadweight loss maximizes consumer and producer surplus, leading to an efficient allocation of resources.
Strategic Considerations in Competitive Markets
Firms in competitive markets without deadweight loss employ various strategies to gain a competitive advantage:
- Product differentiation: Creating unique features or attributes to distinguish products
- Innovation and technological advancements: Developing new products or processes to meet changing consumer demands
These strategies allow firms to increase market share and profitability while contributing to market efficiency.
Policy Implications for Competitive Markets
Government policies play a role in promoting competition and reducing deadweight loss:
- Antitrust laws and regulations: Prevent monopolies and other anti-competitive practices
- Deregulation: Removing barriers to entry and promoting market liberalization
Government intervention can improve market efficiency, but it must be carefully balanced to avoid unintended consequences.
Query Resolution: In A Competitive Market When There Is No Deadweight Loss
What is deadweight loss?
Deadweight loss refers to the reduction in economic welfare that occurs when the quantity of goods or services produced and consumed is below the optimal level.
What are the causes of deadweight loss in competitive markets?
Deadweight loss in competitive markets can be caused by factors such as price ceilings, price floors, taxes, and subsidies.
What are the conditions necessary for a competitive market to operate without deadweight loss?
For a competitive market to operate without deadweight loss, it must meet certain conditions, including a large number of buyers and sellers, perfect information, and the absence of barriers to entry and exit.