PALS Precourse Self-Assessment Rhythm Identification: A Comprehensive Guide introduces a thorough exploration of the significance, methods, and techniques involved in rhythm identification within the context of PALS precourse self-assessment. This guide serves as a valuable resource for individuals seeking to enhance their rhythm identification skills and deepen their understanding of musical rhythms.
The guide delves into the various types of rhythms encountered in music, examining their characteristics, tempo, meter, and beat patterns. It also provides practical techniques for identifying rhythms, utilizing visual cues like notation and rhythm charts, as well as auditory cues like clapping, tapping, and counting.
Precourse Self-Assessment Rhythm Identification
Precourse self-assessment rhythm identification is a crucial practice that enables musicians to evaluate and enhance their rhythm recognition skills. By engaging in self-assessment, individuals can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to strengthen their rhythmic proficiency.
Various methods and techniques can be employed for precourse self-assessment. One common approach involves utilizing a metronome to establish a steady tempo. Musicians can practice playing simple rhythms along with the metronome, gradually increasing the complexity of the rhythms as their accuracy improves.
Another effective technique is to use a rhythm chart or notation to visualize the rhythm. By analyzing the visual representation, musicians can gain a deeper understanding of the beat patterns and note durations. Additionally, clapping, tapping, and counting can be used as auditory cues to reinforce the rhythmic structure.
Precourse self-assessment can significantly enhance rhythm identification skills. By regularly practicing and evaluating their performance, musicians can develop a strong internal sense of rhythm and improve their ability to sight-read and perform music accurately.
Types of Rhythms and Their Characteristics
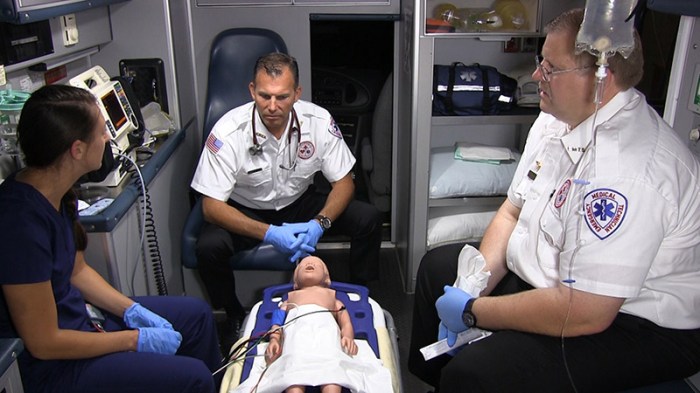
Music encompasses a vast array of rhythms, each with its unique characteristics. The most common types of rhythms include:
- Simple rhythms:Consist of regular, evenly spaced beats, such as 2/4 or 4/4 time.
- Compound rhythms:Group beats into triplets or dotted notes, creating a sense of syncopation, such as 6/8 or 12/8 time.
- Polyrhythms:Involve playing two or more independent rhythms simultaneously, such as 3/4 against 4/4 time.
- Syncopated rhythms:Emphasize off-beats or unexpected accents, creating a sense of rhythmic displacement.
- Asymmetrical rhythms:Feature irregular beat patterns that do not fit into traditional time signatures, such as 5/8 or 7/8 time.
Techniques for Rhythm Identification
Effective rhythm identification techniques are essential for musicians to develop accurate and consistent rhythmic skills. These techniques include:
- Visual cues:Utilizing notation or rhythm charts to visualize the rhythmic structure.
- Auditory cues:Clapping, tapping, or counting to reinforce the beat patterns.
- Subdivision:Breaking down complex rhythms into smaller units to facilitate comprehension.
- Grouping:Identifying patterns of beats and grouping them into measures or phrases.
- Comparison:Analyzing different rhythms and comparing their characteristics to enhance discrimination.
Challenges and Strategies for Rhythm Identification
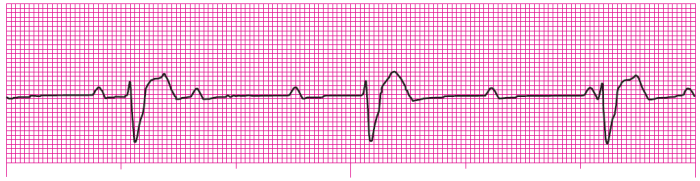
Rhythm identification can present challenges, but with the right strategies, musicians can overcome these obstacles and improve their accuracy. Common challenges include:
- Tempo fluctuations:Maintaining a steady tempo can be difficult, especially when performing complex rhythms.
- Syncopation:Recognizing and interpreting off-beats and unexpected accents can be challenging.
- Polyrhythms:Coordinating multiple independent rhythms simultaneously requires advanced rhythmic skills.
- Asymmetrical rhythms:Comprehending irregular beat patterns can be difficult without proper training.
Strategies for overcoming these challenges include:
- Practice with a metronome:Establishing a consistent tempo is crucial for rhythm accuracy.
- Use visual aids:Notation or rhythm charts can help visualize syncopated or complex rhythms.
- Break down rhythms:Divide complex rhythms into smaller units to facilitate comprehension.
- Listen attentively:Focus on the rhythmic patterns and identify any deviations or irregularities.
- Seek feedback:Request feedback from a teacher or experienced musician to identify areas for improvement.
Applications of Rhythm Identification: Pals Precourse Self-assessment Rhythm Identification
Rhythm identification plays a vital role in various musical contexts:
- Performance:Accurate rhythm identification is essential for executing music with precision and maintaining ensemble cohesion.
- Composition:Understanding different rhythms enables composers to create compelling and engaging musical pieces.
- Music education:Rhythm identification is a fundamental skill that students must develop to comprehend and perform music effectively.
- Music theory:Analyzing rhythms is crucial for understanding the structure and organization of music.
- Music therapy:Rhythm identification can be used as a therapeutic tool to improve coordination, memory, and cognitive function.
FAQ Corner
What is the purpose of PALS precourse self-assessment in rhythm identification?
PALS precourse self-assessment helps individuals assess their current rhythm identification skills, identify areas for improvement, and develop personalized practice strategies.
What are some common challenges in rhythm identification?
Common challenges include distinguishing between similar rhythms, identifying complex rhythms, and maintaining a consistent tempo.
How can I improve my rhythm identification accuracy?
Regular practice using various techniques, such as clapping, tapping, and counting, can enhance accuracy and consistency in rhythm identification.