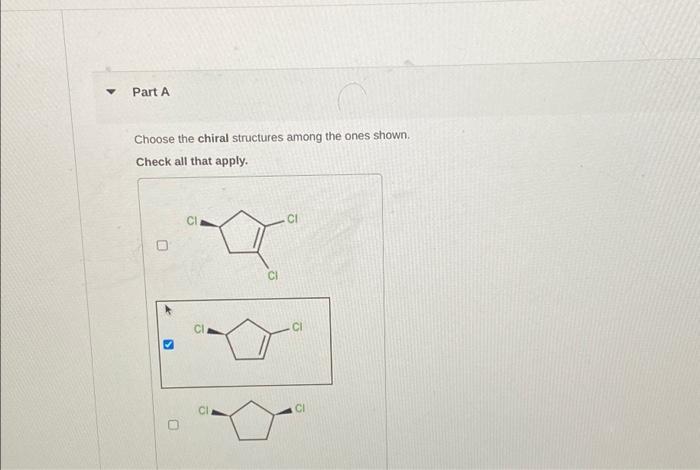
Choose the chiral structures among the ones shown. – In the realm of chemistry, chirality plays a pivotal role in determining the properties and behavior of molecules. Choose the chiral structures among the ones shown, and delve into the fascinating world of molecular asymmetry, where mirror-image molecules exhibit distinct physical and biological characteristics.
Chirality, a fundamental concept in stereochemistry, refers to the non-superimposable mirror-image relationship between two molecules. Enantiomers, pairs of chiral molecules, possess identical molecular formulas but differ in their spatial arrangement, akin to left- and right-handed gloves.
Understanding Chirality
Chirality is a fundamental property of molecular structures that describes their asymmetry and lack of mirror symmetry. It plays a crucial role in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine.
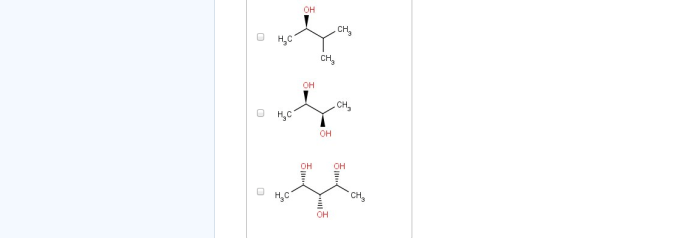
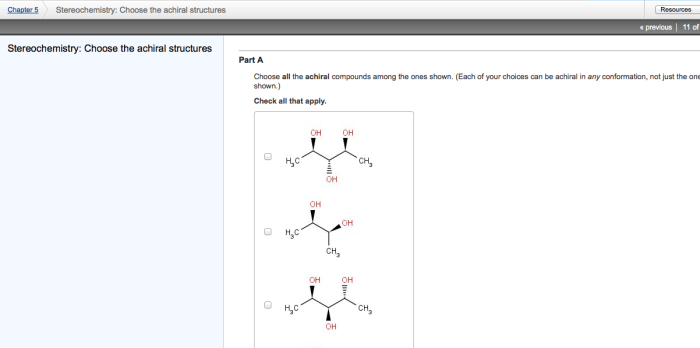
Molecules with a chiral center, also known as a stereogenic center, have two or more non-identical groups attached to the same atom. These molecules exist as two non-superimposable mirror images, called enantiomers. Enantiomers have the same chemical formula and connectivity but differ in their spatial arrangement.
Diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other. They have different physical and chemical properties, unlike enantiomers, which have identical physical properties and differ only in their interaction with chiral molecules.
Identifying Chiral Structures
To identify chiral centers in molecules, look for atoms with four different groups attached. These atoms are typically carbon atoms with tetrahedral geometry.
Common functional groups that can create chirality include:
- Alcohols (-OH)
- Amines (-NH2)
- Epoxides
- Carboxylic acids (-COOH)
- Aldehydes (-CHO)
- Ketones (-C=O)
Methods for Determining Chirality, Choose the chiral structures among the ones shown.
Various techniques can be used to determine the chirality of molecules:
- Spectroscopic techniques:NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) and IR (Infrared) spectroscopy can provide information about the molecular structure and the presence of chiral centers.
- Chromatographic methods:HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) and GC (Gas Chromatography) can be used to separate enantiomers based on their different interactions with chiral stationary phases.
Examples of Chiral Structures
| Name | Structure | Functional Group |
|---|---|---|
| Alanine | CH3CH(NH2)COOH | Amino acid |
| Ibuprofen | C13H18O2 | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug |
| Limonene | C10H16 | Terpene |
Applications of Chirality
Chirality is a crucial factor in drug design and development. Many drugs exist as enantiomers, and their biological activity can differ significantly depending on their chirality.
In natural products and biological systems, chirality plays a vital role in molecular recognition and interactions. For example, enzymes are chiral and can only interact with specific enantiomers of substrates.
FAQ Compilation: Choose The Chiral Structures Among The Ones Shown.
What is the significance of chirality in drug design?
Chirality is crucial in drug design as enantiomers can exhibit different pharmacological properties, toxicities, and metabolic pathways, affecting drug efficacy and safety.
How can we determine the chirality of a molecule?
Spectroscopic techniques (e.g., NMR, IR) and chromatographic methods (e.g., HPLC, GC) are commonly used to determine the chirality of molecules.